What is stakeholder analysis?
A stakeholder analysis is a critical tool for any organisation. It allows for the identification and understanding of the interests and concerns of the different groups that have a stake in an organisation’s success. This understanding will enable the management of those groups to meet their needs effectively.
There are several things to consider when performing a stakeholder analysis. First, it’s essential to identify all the groups that could be affected by your decisions or actions. This includes customers, employees, shareholders, suppliers, regulatory bodies, and community members. Second, it’s also essential to understand each group’s objectives and priorities. This will help you determine which issues are most important to them and how best to address them.
If you want to ensure a successful stakeholder analysis, be prepared to spend time gathering data and talking with stakeholders.
Stakeholder analysis and investment
Before making any new investment, a few key things need to happen: first, the data needs to be analysed and interpreted to develop a plan; second, stakeholders need to be convinced that the investment is worthwhile and will help meet shared goals; and finally, the necessary approvals must be obtained.
Although these steps may seem straightforward, they can sometimes be challenging to carry out unless everyone involved is on board – which is where stakeholder support comes in. Some stakeholders can be helpful and supportive like any other group, while others can become obstructive. However, by understanding how these groups operate and tailoring communications accordingly, you can ensure that progress continues without inappropriate interference.
Stakeholders and risk management
Risk management involves considering potential organisational risks and allocating resources to minimise or avoid adverse effects. Stakeholders are people or organisations who may be affected by a decision, treatment, strategy, or process. They can be individual employees, business partners, suppliers, or customers. At any time during the risk management process, stakeholders may have different opinions about what risks should be considered and how best to manage them.

So, who is a stakeholder?
A stakeholder is any group with a direct or indirect stake in your organisation’s success. This could include customers, employees, shareholders, suppliers, regulatory bodies, and community members.
How to gain early alignment among all stakeholders on goals and plans
Achieving early alignment among all stakeholders on goals and objectives is one of the most critical steps in conducting a successful stakeholder analysis. This process helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and understands the objectives and goals of your organisation.
There are several ways to achieve early alignment. You can meet with all stakeholders, discuss critical issues in detail, or create a feasibility study. Whatever approach you choose, be sure to gather as much data as possible. This will help you make informed decisions about how best to proceed with your stakeholder analysis.
What are stakeholder identification techniques?
Several stakeholder identification techniques can be used to identify all the groups that could be affected by your decision or action. These include stakeholder interviews, focus groups, and surveys.
Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages. For example, stakeholder interviews are good for getting detailed information from a few people. However, they can be time-consuming and challenging to conduct. Focus groups are good for getting feedback from a large number of people in a short amount of time. However, they can be subjective and biased. Surveys are good for getting general feedback from a large number of people. However, they can be expensive and challenging to conduct.
Whichever stakeholder identification technique you choose, use targeted resources to ensure accurate results.
Why should product/service managers conduct a stakeholder analysis?
A stakeholder analysis is a vital tool for product/service managers because it helps to ensure the needs of all relevant groups are considered. By understanding the objectives and priorities of all potential stakeholders, managers can ensure that their products or services meet the needs of everyone involved.
How does conducting a stakeholder analysis help to achieve goals?
Understanding the objectives and priorities of all potential stakeholders can help organisations ensure that their products or services meet the needs of everyone involved. This ensures everyone is aligned with the organisation’s goals and plans and that concerns are addressed early in the development process.
What are the four steps of stakeholder analysis?
There are four steps to conducting a successful stakeholder analysis:
1. Identify your stakeholders. This step involves understanding who is essential to your organisation and their goals, objectives, and priorities.
2. Assess your organisation’s impact on these stakeholders. Once you have identified them, you must determine how your organisation will impact them. This includes considering any potential benefits and threats.
3. Consult with these stakeholders. Once you have determined your organisation’s impact on your stakeholders, it’s time to consult with them about their concerns and expectations. This allows everyone involved to understand the ramifications of your organisation before anything happens.
4. Resolve any conflicts. If stakeholders have disagreements about how your organisation should proceed, resolve them through discussions or negotiations.
Stakeholder analysis template
There is no one-size-fits-all template for conducting a stakeholder analysis, as the process will vary depending on the organisation and the stakeholders involved. However, some tips to keep in mind when conducting a stakeholder analysis include the following:
1. Gathering as much data as possible – When conducting a stakeholder analysis, gathering as much information about your organisation and its stakeholders is vital. This includes collecting data about stakeholder objectives, priorities, and concerns.
2. Considering the implications – Once you have gathered all the data necessary for stakeholder analysis, it is crucial to consider your organisation’s impact on these stakeholders. This includes weighing any threats and benefits associated with the organisation.
3. Consultation with stakeholders – After determining your organisation’s impact on stakeholders, consult them about their concerns and expectations.
When to use a stakeholder analysis matrix?
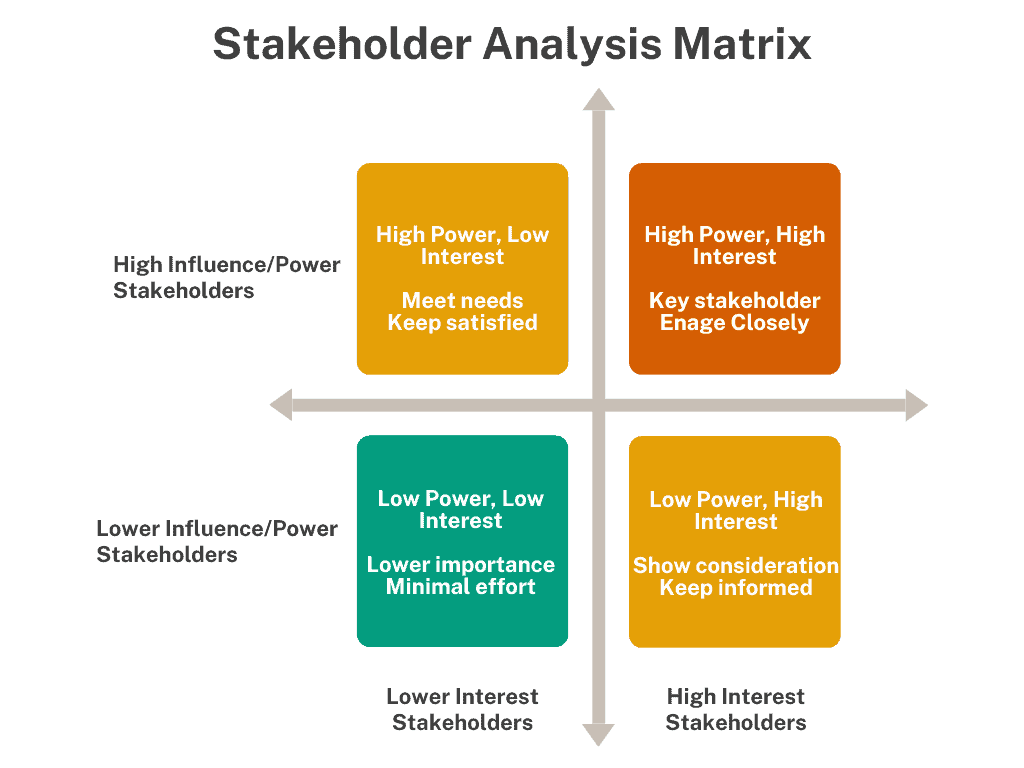
When conducting a stakeholder analysis, stakeholders should be identified, and their interests and needs assessed. A stakeholder analysis matrix is a valuable tool for identifying and evaluating the interests and influence of different groups of stakeholders. The matrix can help identify which groups are most important to success and determine how vital their concerns are.
An example of a stakeholder analysis matrix is below:
Identify your stakeholders
The first step in creating a stakeholder analysis matrix is identifying all stakeholders in your organisation. To do this, you must gather a list of all the people who impact your organisation. This could include employees, clients, partners, and even suppliers.
Once you have a list of all the stakeholders, it is time to assess their impacts on your organisation. This can be done by evaluating their organisation roles, level of involvement, and potential concerns or risks.
The most common stakeholders are:
- Government stakeholders
- Shareholders
- Investors
- Senior executives
- Managers
- Supervisors
- Colleagues
- Partners
- Suppliers
- A segment of the public
Questions to be answered include:
- What is their role in the organisation?
- What are their concerns or risks related to the organisation?
- What are their expectations from the organisation?
- How will the organisation impact them?
Understand your key stakeholders
Once you have created the matrix, it is essential to understand each stakeholder’s role in the organisation and their expectations. This will help you better manage and communicate with them throughout the organisation.
The tools you need to keep stakeholders informed
To effectively use a stakeholder analysis matrix, you will need to have the following tools at your disposal:
- A list of all stakeholders involved in your organisation
- A data collection tool
- A stakeholder analysis matrix
- Communication tools
- Negotiation skills
- Time
- Patience
Now that you know what a stakeholder analysis matrix is and what it can do for your organisation, it is time to learn how to create one. With the right tools and preparation, a stakeholder analysis matrix will help ensure all stakeholders are on the same page and that any concerns or risks are considered.
Group and prioritise these stakeholders
Once you have identified and assessed the stakeholders’ impacts and concerns, it is time to group them based on their impact and importance. This will help to determine which stakeholders should be prioritised when communicating with them.
Finally, you can prioritise these stakeholders based on their impact and importance. This will help you better manage the organisation and ensure all key stakeholders are considered.
Address conflicts early on
Prioritising and managing conflicts with stakeholders is critical to ensuring a successful organisation. By addressing conflicts early on, you can avoid potential disputes and ensure that the organisation moves forward smoothly.
Find out how to communicate with and win buy-in from each type of stakeholder
Now that you have completed a stakeholder analysis, it is time to learn how to communicate with and win buy-in from each type of stakeholder. By understanding their role in the organisation, expectations, and concerns, you will be better equipped to manage them effectively throughout the organisation.
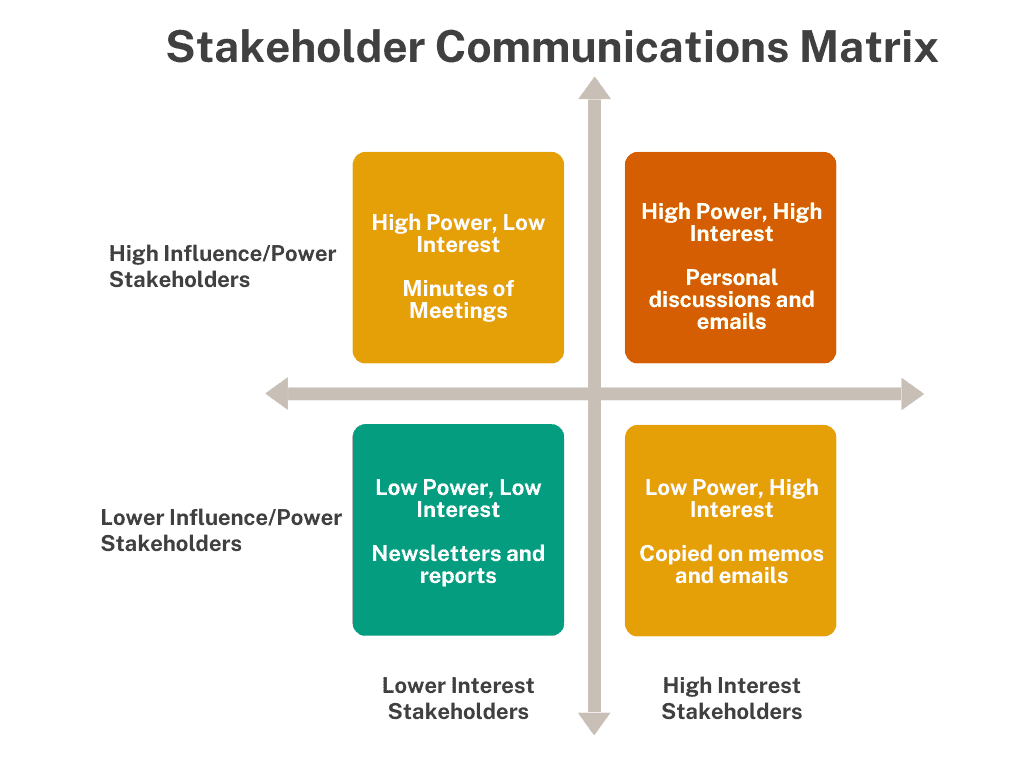
An example of a communication matrix is below: